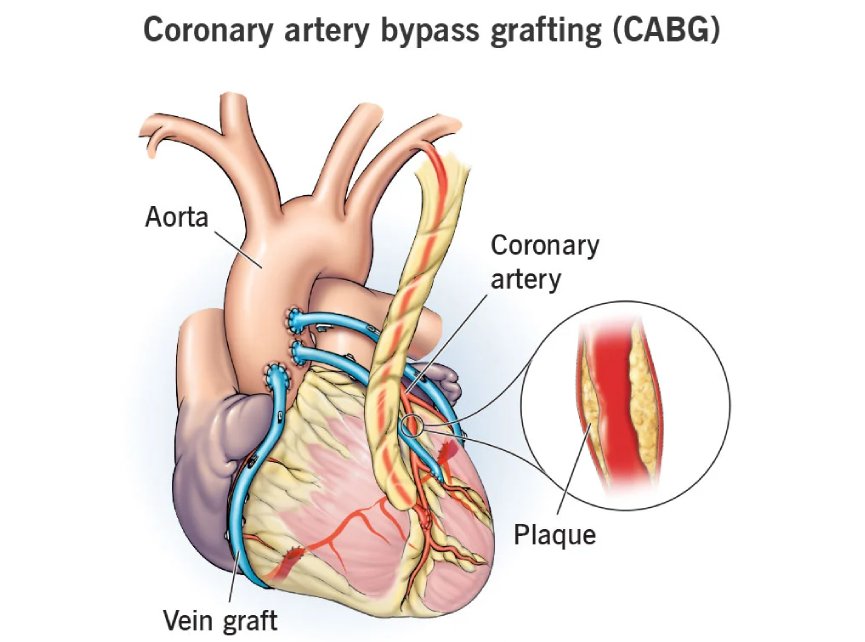
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), also called as heart bypass surgery, is a procedure which restores blood flow to areas of your heart that aren’t getting enough blood because of the blocked heart artery.
Artery blockages can cut off blood flow, causing heart attacks or heart attack-like symptoms. CABG restores blood flow by using blood vessels from other parts of your body to create a diversion around blockages.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) is done to treat patients with severe Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also called Coronary Artery Disease. It is used to improve blood flow to the heart.
The function of the heart arteries is to supply oxygen-rich blood to your heart, in CHD a substance made of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other elements called plaque gets piled up in the arteries of the heart leading to the blockage of the arteries.
In CABG, the blocked arteries are bypassed using a blood vessel graft to restore the heart's regular blood flow. By making a new passageway and rerouting blood flow around blocked arteries through CABG, the purpose to increase the blood supply to the heart muscle is achieved.
The blood vessel graft is typically taken from the chest, arm, or leg.
Symptoms of Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) may include:
Before the surgery, your surgeon will discuss with you about all aspect of the surgery and you will have a chance to ask questions you have in mind about the procedure. As the procedure is carried out using a general anaesthetic where you will be asleep during the operation, you will be asked to not eat or drink for 8 hours before the procedure, generally after midnight.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or think you could be and if you are sensitive to or are allergic to any medicines, iodine, latex, tape, or anaesthetic medicines (local and general). Tell your doctor about all medicines (vitamins, herbs, and supplements) that you are taking.
If you have a history of bleeding issues or are using aspirin, blood-thinning medications, or any other medications that impact blood clotting, let your doctor know. You may be asked to stop some of these medications prior to the surgery.
Prior to the surgery, you will undergo investigations and diagnosis tests such as:
Your surgeon will decide which investigations and tests are required before the surgery.
Coronary artery bypass graft surgery usually lasts 3 to 6 hours. But it may take longer depending on how many blood vessels are being attached.
Blood vessels can be taken from your leg (saphenous vein), inside your chest (internal mammary artery), or your arm (radial artery).
You will be put into a deep sleep before to this surgery, as with most major surgeries. As a result, you experience no pain during the procedure. Additionally, it makes you more relaxed for subsequent preparatory steps.
Because CABG involves heart surgery, various forms of life support are frequently used such as:
In CABG, the blocked arteries are bypassed using a blood vessel graft to restore the heart's regular blood flow. A blood vessel from another part of your body, such as your leg, arm, or chest, is taken in order to create the bypass (detour) around the obstruction using the blood vessel as graft. Multiple bypasses may be required when there are multiple blocked arteries. These are bypasses that are double (2), triple (3), and quadruple (4).
Surgeons prefer to take blood vessel from your chest (internal mammary artery) because it doesn't narrow over time, unlike the blood vessels taken from your leg or arm
Once all the graft vessels have been removed, your, the cardiac surgeon will make a long cut in the centre of your chest and opens the rib cage. Your heart will be temporarily kept at a standstill during the procedure and with the help of a heart-lung machine the blood keeps flowing through your body.
Once they get access to your heart, the surgeon will craft the bypass using the harvested blood vessel. The upper end of the bypass is attached to your aorta (the large artery that carries blood out of your heart and to the rest of your body) just after it exits your heart. The lower end of the bypass will be attached to the blocked artery just past the blockage.
After the grafts are in place, your heart will be restarted using controlled electrical shocks and the blood will starts circulating to your heart through your new graft. At the end, the surgeon will close the rib cage and close the incision with stitches and staples.
While CABG frequently employs the same techniques on the majority of patients, there are times when other approaches are preferable for your individual circumstances. There are several variations of this procedure:
In this procedure, the surgeon uses surgical robots to perform CABG surgery. To carry out the surgery, the surgeon drives the robotic arms, controls the robot's movements while performing TECAB. An endoscope is attached to the robotic arms so that the surgeon can watch inside the body and view the results of the surgery on a screen.
During a TECAB grafting procedure, the surgeon makes smaller incisions and get access to the heart through the gaps between some of the ribs instead of making large incision to open the sternum and rib cage. In TECAB heart-lung bypass machine can be used or it can be done off-pump. This is also called Robot-assisted CABG.
After your procedure, you may need to stay in the intensive care unit for 1 to 2 days. Medical personnel will need to keep an eye on your condition and look for signs of complications. After you are discharged from the intensive care unit, you will need to spend 5-7 days in the hospital.
Four to six weeks are required for recovery following surgery, depending on the patient's overall health.
After the procedure, the doctor might recommend anti-arrhythmics, anti-coagulants, and painkillers.
There may be some side effects during and after the surgery. They can include: